Introduction to Gandhara, Pakistan
Nestled in the northwest corner of Pakistan, Gandhara is an ancient region steeped in history and cultural significance. Renowned for its rich heritage, this enchanting land holds a pivotal place in the annals of human civilization. Situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, Gandhara has been a melting pot of diverse cultures, making it a treasure trove of archaeological wonders and captivating narratives.
Gandhara’s historical prominence can be traced back to antiquity, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Neolithic era. However, it was during the 6th century BCE that the region witnessed a significant transformation with the spread of Buddhism. Under the patronage of Emperor Ashoka, numerous stupas, monasteries, and sculptures were constructed, solidifying Gandhara’s status as a flourishing center of Buddhist learning.
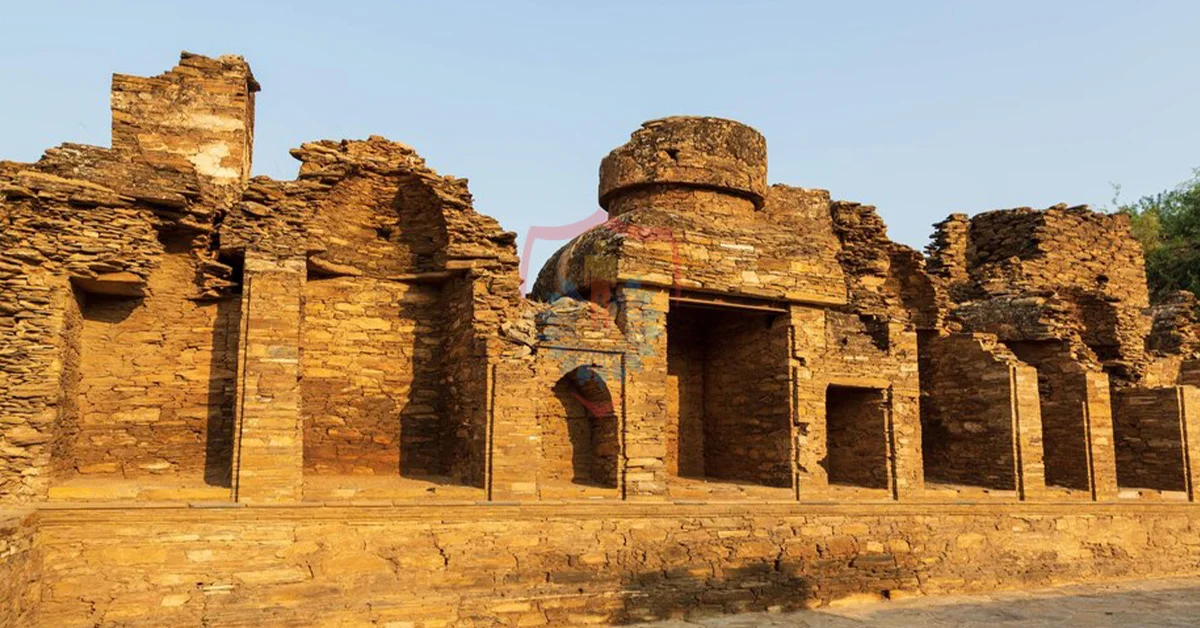

One of the most remarkable aspects of Gandhara is its exceptional artistry, which blossomed during the 1st to 5th centuries CE. The Gandhara school of art, influenced by Hellenistic and Roman styles, produced intricate sculptures and reliefs, often depicting scenes from the life of Buddha. These masterpieces serve as a testament to the harmonious fusion of diverse artistic traditions.
In modern times, Gandhara continues to captivate scholars, historians, and tourists alike. Archaeological excavations have unearthed an array of artifacts, providing valuable insights into the region’s past and its interactions with neighboring civilizations. Today, visitors can explore ancient sites like Taxila, Peshawar, and Swat to experience firsthand the grandeur of Gandhara’s heritage.
The Enigmatic Land of Gandhara
Gandhara, once an ancient kingdom, encompassed parts of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan. Flourishing as a cultural and religious hub, it served as a vital crossroads of trade and cultural exchange. The region’s cosmopolitan nature led to the blending of various influences from the Greeks, Persians, Indians, and Central Asians, creating a unique and dynamic tapestry of culture.
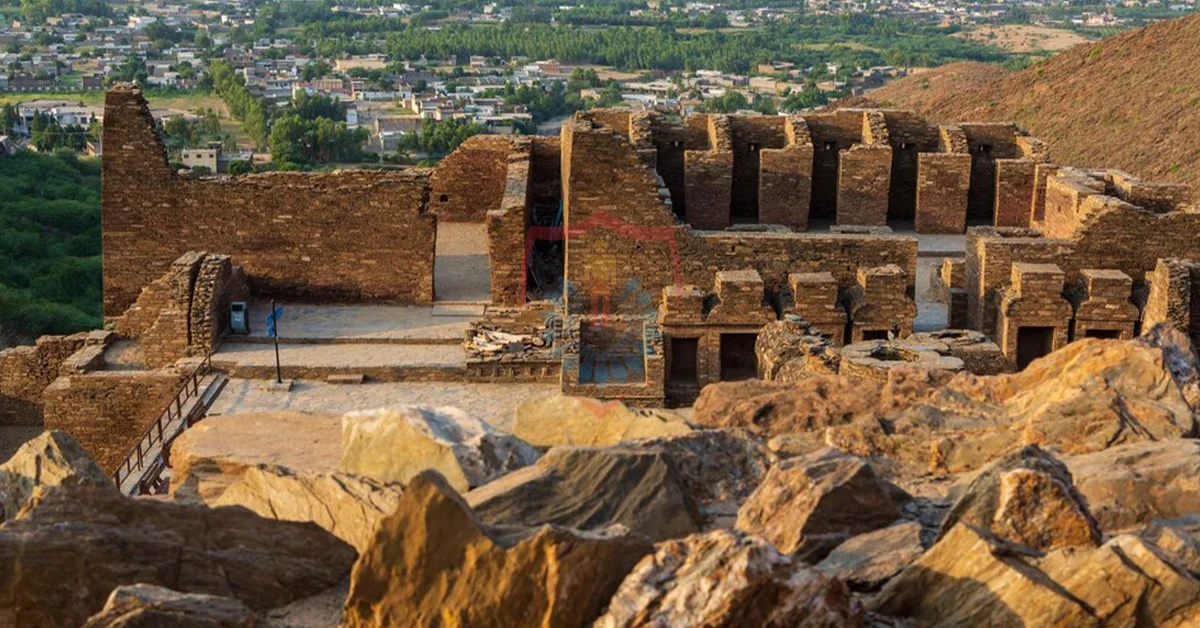

Gandharan Art: A Fusion of Cultures
At the heart of Gandhara’s historical legacy lies its distinctive artistic style – Gandharan art. This remarkable art form emerged as a fusion of Hellenistic and Indian elements, showcasing the harmonious coexistence of Greek artistic techniques and Buddhist symbolism.
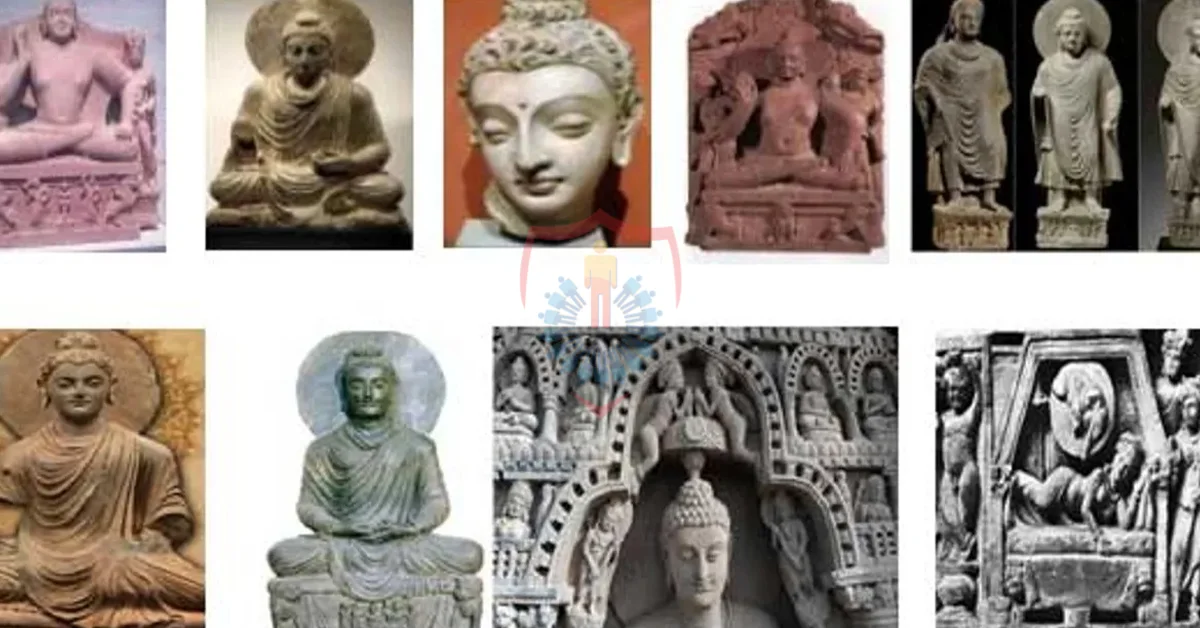

Gandharan artists were renowned for their exceptional craftsmanship in sculpting lifelike representations of Buddha and Buddhist deities. The intricate drapery and realistic human forms imbued these sculptures with an ethereal aura, inviting contemplation and awe.
Rediscovering Gandharan Sculptures
The most iconic relics of Gandhara are undoubtedly its exquisite sculptures. The ancient city of Taxila, a vital center of Gandharan art, housed a treasure trove of sculptures that have withstood the test of time. These sculptures, often carved in stone, bear witness to the artistic prowess of ancient Gandhara.
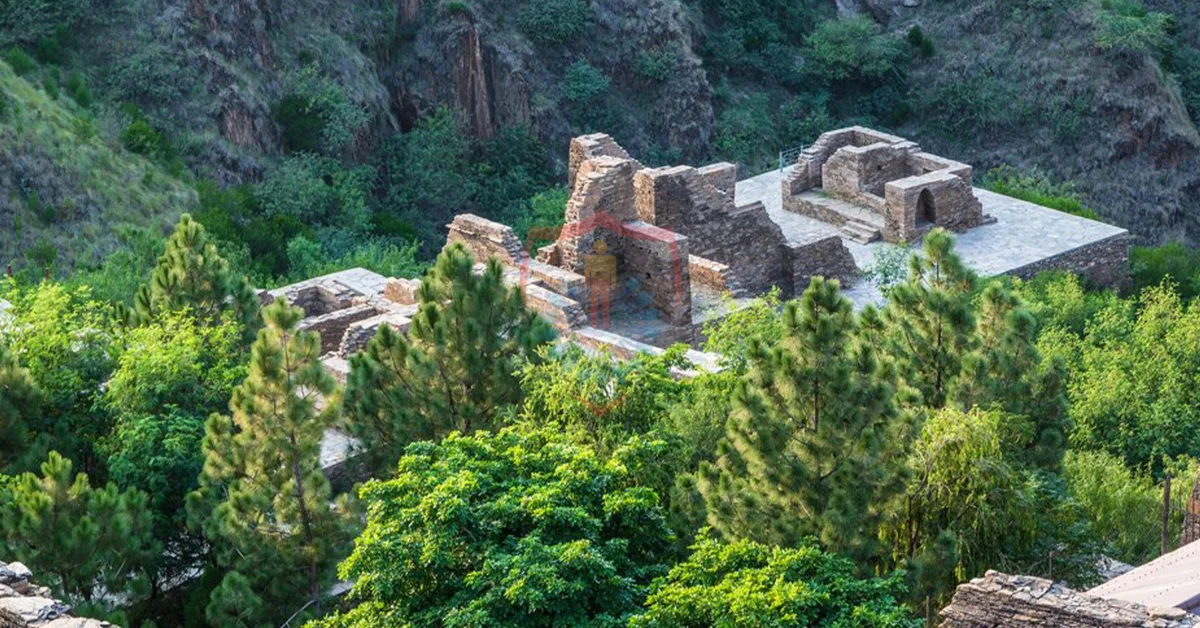

The depictions of Buddha, adorned with serene and compassionate expressions, evoke a sense of spiritual enlightenment. As visitors behold these sculptures, they are transported to an era when art and faith merged seamlessly to create captivating masterpieces.
The Greco-Buddhist Connection
The Greco-Buddhist connection in Gandhara is a fascinating chapter in the region’s history. As the Hellenistic influence spread across the land following the conquests of Alexander the Great, it encountered the blossoming Buddhist faith. This encounter gave rise to an intriguing blend of Greek and Buddhist art forms, evident in the representation of Buddha with a Greek aesthetic.
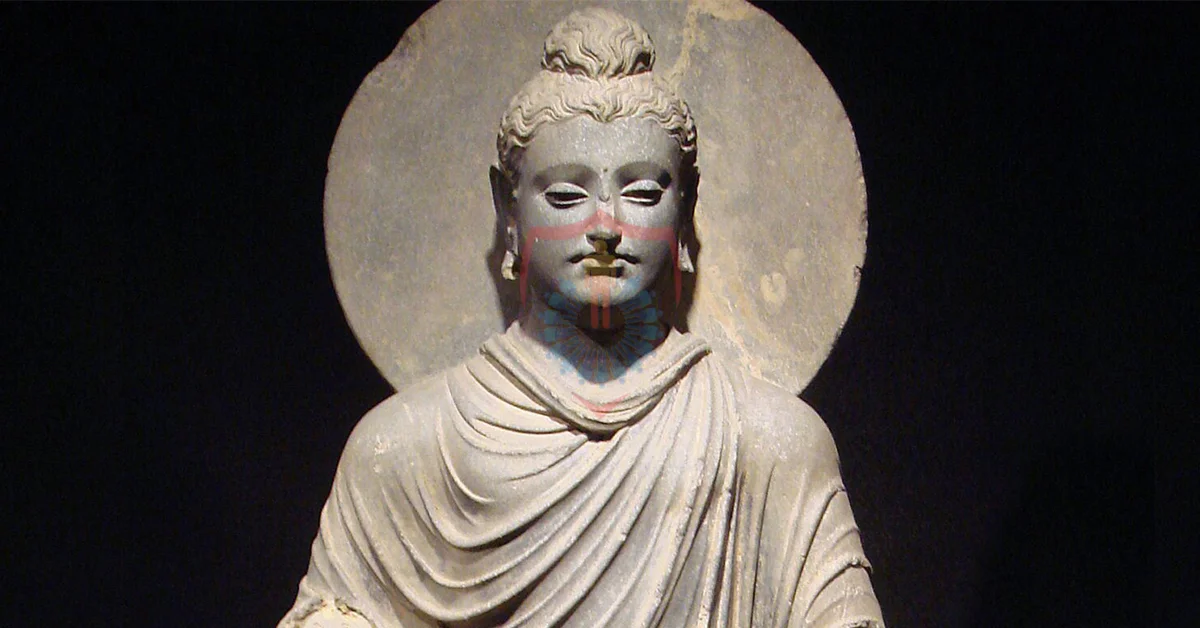

This artistic fusion not only reflected the openness of Gandhara to diverse influences but also served as a bridge between East and West. The Greco-Buddhist art, found in Gandhara’s stupas and monasteries, played a significant role in promoting cultural exchange along the ancient Silk Road.
Unearthing the Rich History of Gandhara
Gandhara, an ancient region situated in what is now modern-day Pakistan and parts of Afghanistan, boasts a rich and captivating history that continues to intrigue historians and archaeologists alike. The region’s legacy spans several millennia, making it a crucial crossroads of culture and civilization. Gandhara’s history is deeply entwined with the rise and fall of empires, most notably the Mauryan, Greco-Bactrian, and Kushan empires. As scholars delve into its archaeological treasures, they unearth fascinating insights into the region’s art, religion, and societal developments.
One of the most significant aspects of Gandhara’s history is its exceptional artistry, particularly the Gandhara school of art that flourished between the 1st and 5th centuries CE. Influenced by Hellenistic and Roman styles, this unique art form blended Greek, Roman, and Indian elements, producing stunning sculptures and reliefs. These artworks typically depicted Buddhist themes, showcasing the harmonious amalgamation of diverse cultural influences in the region. Gandharan art remains an invaluable source of knowledge about the spread of Buddhism and the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations.
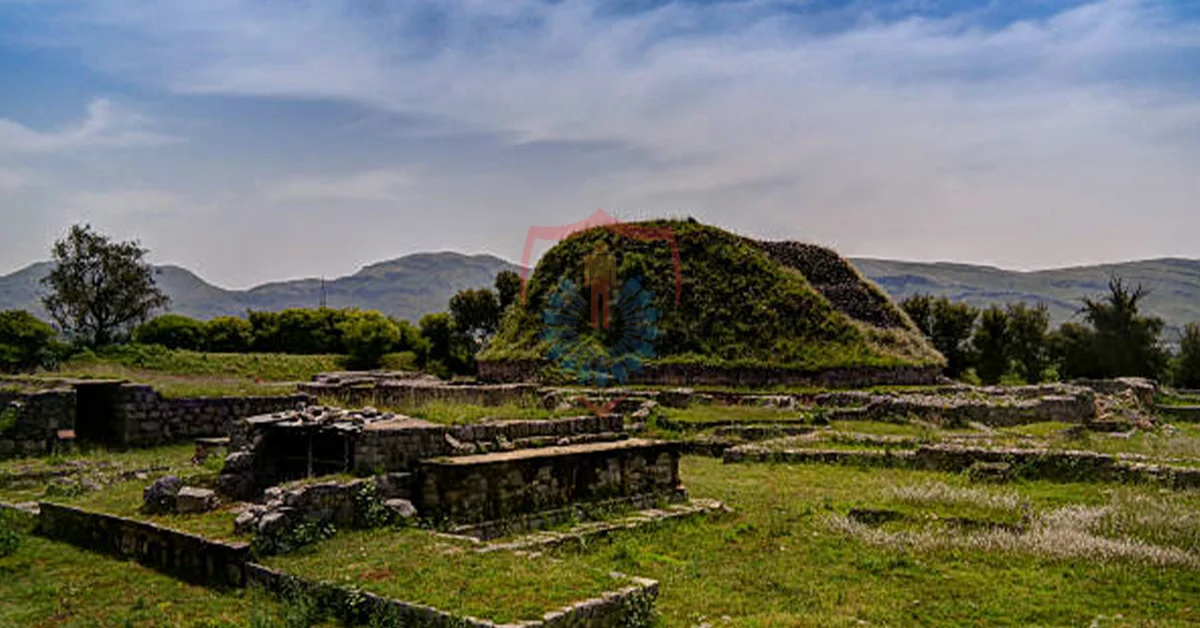

The advent of Buddhism in Gandhara is a crucial chapter in its history. The region played a pivotal role in the early development and dissemination of Buddhist teachings. Notably, Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan dynasty is said to have erected numerous stupas and monasteries in the area to propagate Buddhism. As a result, Gandhara became a thriving center for Buddhist learning, attracting scholars and pilgrims from across Asia. The study of ancient Buddhist texts and inscriptions found in the region provides deep insights into the evolution of Buddhist philosophy and its impact on the local populace.
Gandhara’s strategic location also contributed to its historical significance. Positioned at the crossroads of various trade routes, the region became a melting pot of cultures, languages, and religions. The interactions between diverse communities fostered an atmosphere of intellectual exchange and creativity. The Greco-Bactrian and Kushan empires, who held control over the region, further facilitated the exchange of ideas, further enriching Gandhara’s cultural landscape.
Despite its immense historical importance, much of Gandhara’s history had remained buried beneath the sands of time until the 19th century when British archaeologists began systematic excavations. Since then, numerous archaeological sites have been unearthed, revealing a treasure trove of artifacts, sculptures, and ancient structures. These findings not only shed light on the region’s past but also provide a deeper understanding of the broader historical narratives of South Asia and Central Asia.
In conclusion, unearthing the rich history of Gandhara is an ongoing endeavor that continues to captivate researchers worldwide. The region’s unique blend of art, culture, and religion serves as a testament to the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations and the enduring impact of Buddhism on the subcontinent. As further excavations and research take place, it is likely that more revelations about this ancient land and its contributions to human history will come to light, solidifying Gandhara’s place as a cultural and historical treasure worth preserving and studying for generations to come.
The Mauryan Empire and Ashoka’s Legacy
The Mauryan Empire, one of the most significant ancient Indian dynasties, left an indelible mark on the subcontinent’s history. Established by Chandragupta Maurya in the 4th century BCE, the empire stretched across much of present-day India and neighboring regions. However, it was Emperor Ashoka, Chandragupta’s grandson, who became one of the most renowned and revered rulers of the Mauryan dynasty, leaving behind a legacy that continues to inspire people worldwide.
Ashoka’s reign witnessed a transformative moment in his life following the Kalinga War, which resulted in immense bloodshed and devastation. Deeply moved by the suffering he witnessed, Ashoka underwent a profound conversion to Buddhism and embraced the principles of non-violence, compassion, and religious tolerance. This transformative change led to a radical shift in the empire’s policies, and Ashoka’s principles of Dhamma (righteousness) became the guiding force of his rule.

Ashoka’s legacy lies in his commitment to social welfare and the spread of Buddhist teachings. He initiated a series of projects aimed at improving the lives of his subjects, such as constructing hospitals, building roads, and promoting trade and commerce. His edicts, inscribed on rocks and pillars throughout the empire, served as a form of public communication, conveying his ethical and moral precepts to his people.
Moreover, Ashoka’s influence extended far beyond his empire’s borders. Through his diplomatic efforts, he fostered ties with neighboring kingdoms and even established friendly relations with Hellenistic and Mediterranean powers. His support for Buddhism’s dissemination beyond India’s shores contributed to the religion’s spread across Asia, leaving an enduring impact on the region’s spiritual and cultural landscape.
Silk Road: A Crossroads of Trade and Ideas
Gandhara’s strategic location along the ancient Silk Road made it a crucial crossroads of trade and cultural exchange. The Silk Road facilitated the movement of goods, ideas, and people between the East and the West, fostering a vibrant exchange of knowledge and beliefs.
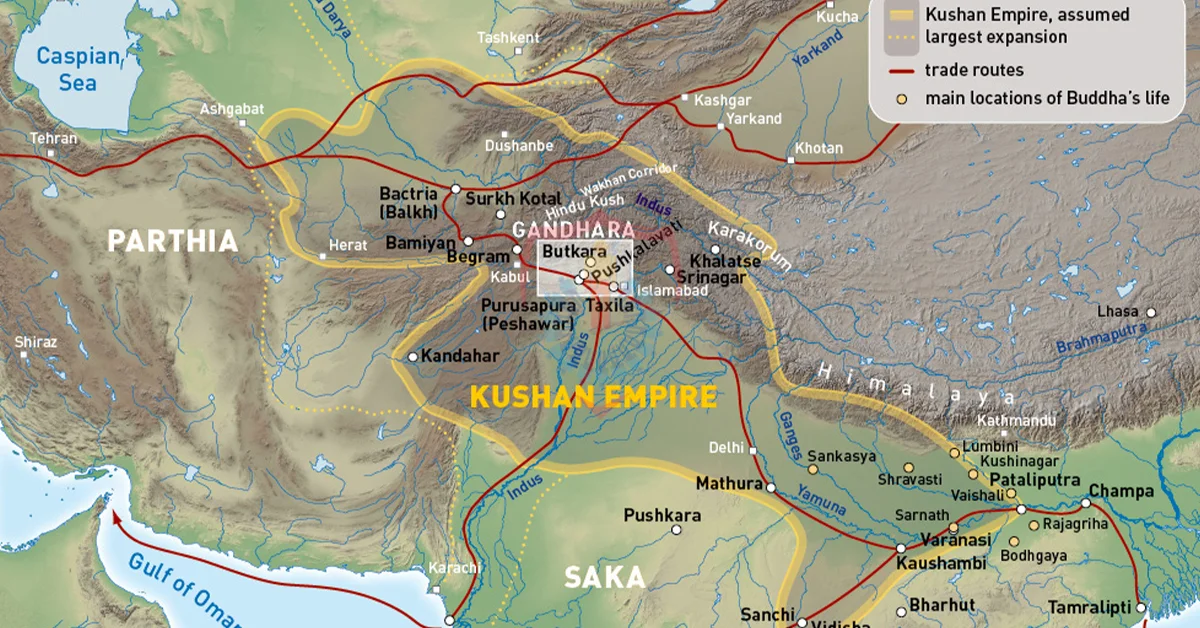
The monasteries and stupas of Gandhara became essential pilgrimage sites for travelers from distant lands, contributing to the global dissemination of Buddhist philosophy. The Silk Road not only facilitated commerce but also acted as a bridge for the transmission of diverse cultures and ideologies.
Rediscovering Gandhara Today
In the present day, the legacy of Gandhara continues to captivate the imagination of people from all over the world, as efforts to rediscover and understand this ancient civilization are ongoing. Archaeologists, historians, and scholars are delving deeper into the rich tapestry of Gandhara’s history, unearthing new treasures and shedding light on its cultural significance. Through advanced archaeological techniques and research, the remnants of this ancient civilization are being meticulously examined, revealing a fascinating mosaic of art, religion, and societal structures.
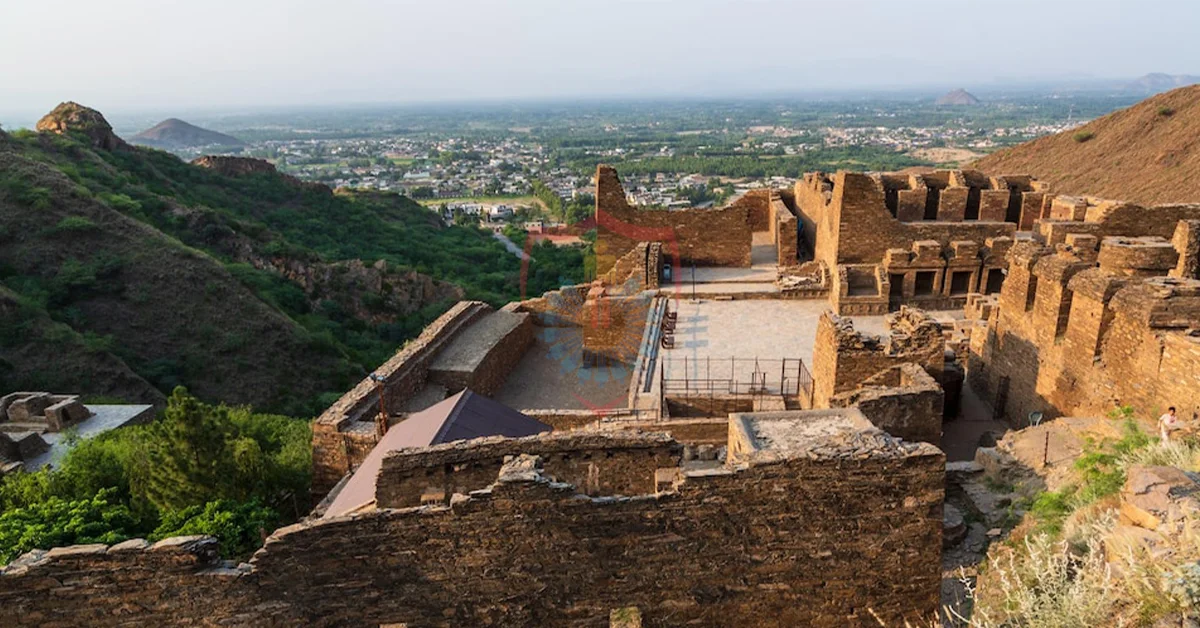

One of the most exciting aspects of rediscovering Gandhara lies in the preservation and restoration of its exquisite art and artifacts. Museums both in Pakistan and abroad proudly display these works of art, allowing people to marvel at the intricate craftsmanship and cultural synthesis that defined Gandhara’s artistic legacy. Not only do these exhibits provide a glimpse into the past, but they also foster a deeper appreciation for the region’s historical contributions to the development of art in South Asia and beyond.
Furthermore, the rediscovery of Gandhara also has significant implications for our understanding of Buddhism’s early history and its spread across the region. Gandhara’s role as a center for Buddhist learning and the arts has been crucial in shaping the religious and philosophical landscape of Asia. Today, scholars and practitioners alike are revisiting Gandhara’s Buddhist heritage, seeking insights into the evolution of the religion and its profound impact on societies throughout history.
Buddhist Tourism in Pakistan
Pakistan, with its rich historical heritage, holds a unique allure for Buddhist tourists seeking to explore the ancient treasures of Gandhara. As a region that played a pivotal role in the early spread of Buddhism, Pakistan offers an exceptional opportunity for visitors to immerse themselves in the footsteps of the Buddha and discover the profound impact of this ancient religion on the subcontinent.
One of the prime destinations for Buddhist tourism in Pakistan is Taxila, an archaeological site of immense historical significance. Once a thriving center of learning and trade during the Gandhara period, Taxila is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Visitors can explore the well-preserved ruins of stupas, monasteries, and universities that once attracted scholars and pilgrims from far and wide. The Dharmarajika Stupa and the Taxila Museum house a remarkable collection of Gandharan art, including intricate sculptures and relics, providing a glimpse into the region’s artistic and spiritual past.
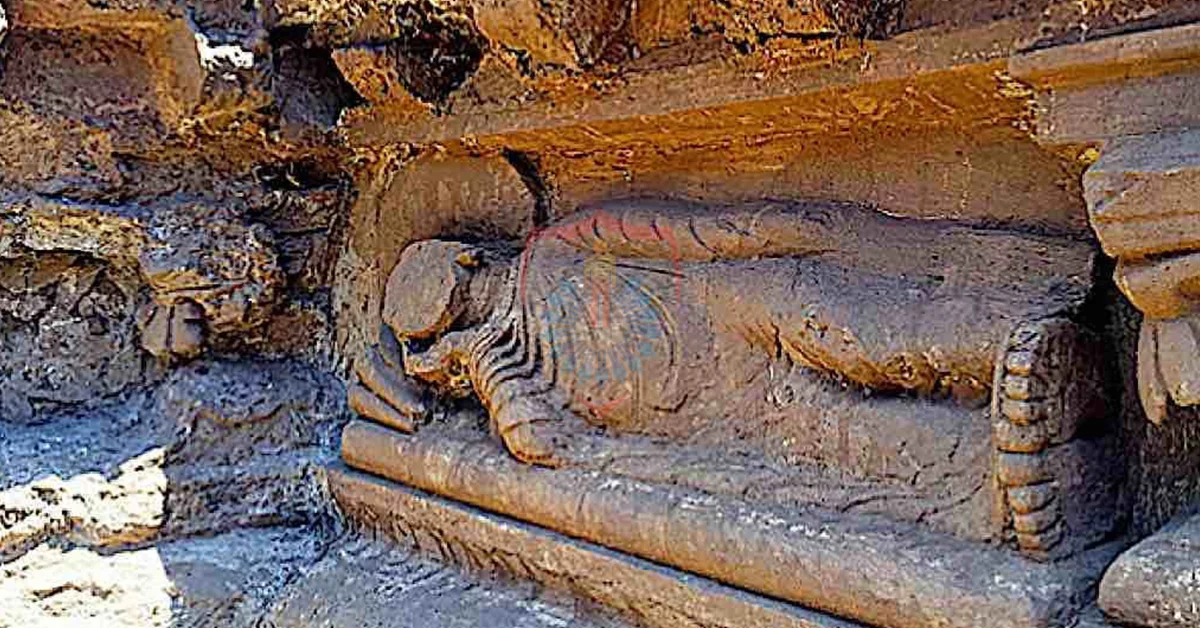

Another prominent site for Buddhist tourists is Swat Valley, often referred to as the “Switzerland of the East.” This picturesque valley is not only known for its natural beauty but also for its historical significance as an important center of Buddhism. The Butkara Stupa and the ruins of the Udegram Buddhist Monastery are among the notable attractions that draw visitors seeking to connect with the roots of Buddhism in this serene setting.
Peshawar, the capital of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, is another crucial stop on the Buddhist tourism trail. The city’s rich history dates back to the Gandhara period, and it was a significant hub for Buddhist art and culture. The nearby archaeological site of Gor Khatri, along with the Peshawar Museum, houses an impressive collection of Gandharan artifacts, providing insights into the region’s cultural and religious heritage.
Buddhist tourism in Pakistan offers a unique blend of historical exploration, spiritual contemplation, and cultural appreciation. As visitors embark on this journey to rediscover the ancient wonders of Gandhara, they not only enrich their understanding of Buddhism’s early history but also witness the beauty of a region that continues to inspire awe and wonder to this day. The preservation and promotion of these historical sites remain essential in showcasing Pakistan’s rich heritage and in fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations.
Preservation Efforts
Preserving the cultural and historical treasures of Gandhara is a collective endeavor undertaken by governments, cultural organizations, and local communities. Recognizing the significance of these ancient artifacts and sites, concerted efforts are being made to safeguard them for future generations. One of the primary strategies is the establishment of museums and galleries dedicated to housing and showcasing Gandharan art and artifacts. These institutions not only protect the delicate sculptures and relics from environmental degradation but also provide educational resources and immersive experiences for visitors to learn about Gandhara’s history and artistic heritage.
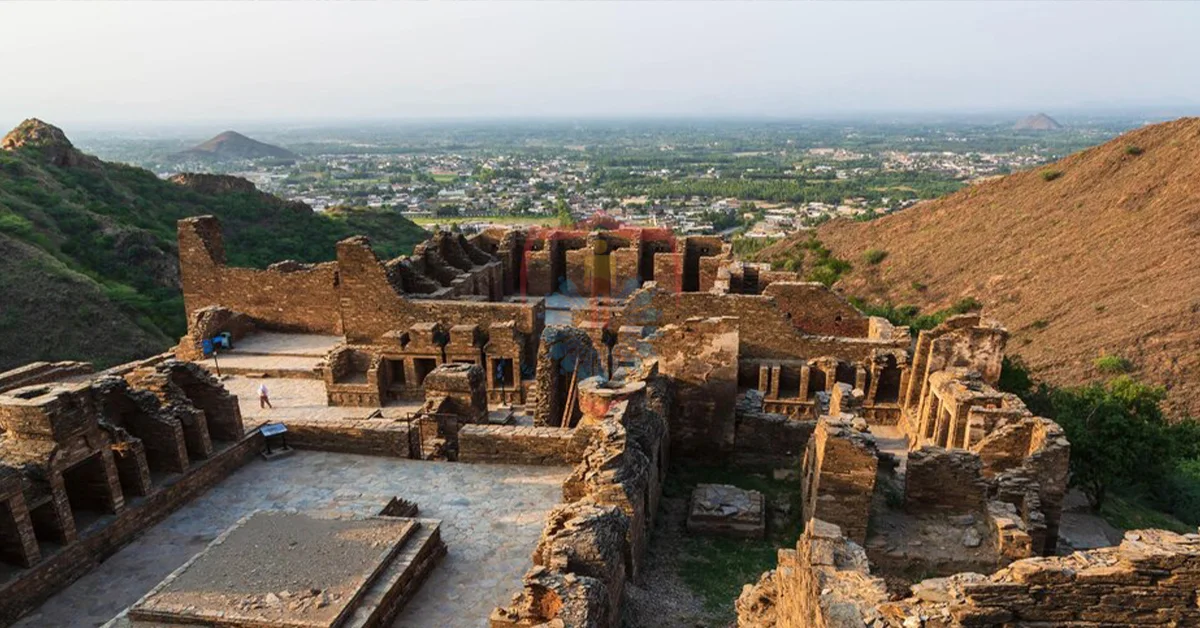

Additionally, stringent conservation measures are put in place to protect archaeological sites and monuments in the Gandhara region. Proper documentation, excavation techniques, and controlled access are employed to prevent damage and ensure that the historical context of each site is preserved. Collaborations between local communities, researchers, and international organizations foster a deeper understanding of the region’s significance, leading to effective preservation strategies that balance tourism and conservation efforts. These endeavors aim to uphold the integrity of Gandhara’s cultural legacy and maintain its allure as a timeless cultural treasure.
Gandhara Art in Modern Times
The exquisite art of Gandhara continues to captivate art enthusiasts and historians in modern times. This ancient art form, which flourished in the region of Gandhara during the 1st to 5th centuries CE, has left a lasting impact on the artistic landscape of South Asia and beyond.
Gandhara art is renowned for its unique amalgamation of Hellenistic, Roman, and Indian artistic influences. This eclectic blend is best exemplified in the intricate sculptures and reliefs that adorned the stupas and monasteries of ancient Gandhara. The sculptures often depicted Buddhist themes, narrating the life and teachings of Buddha and other important figures in the Buddhist pantheon. Today, these masterpieces can be found in museums and private collections, mesmerizing viewers with their artistry and historical significance.
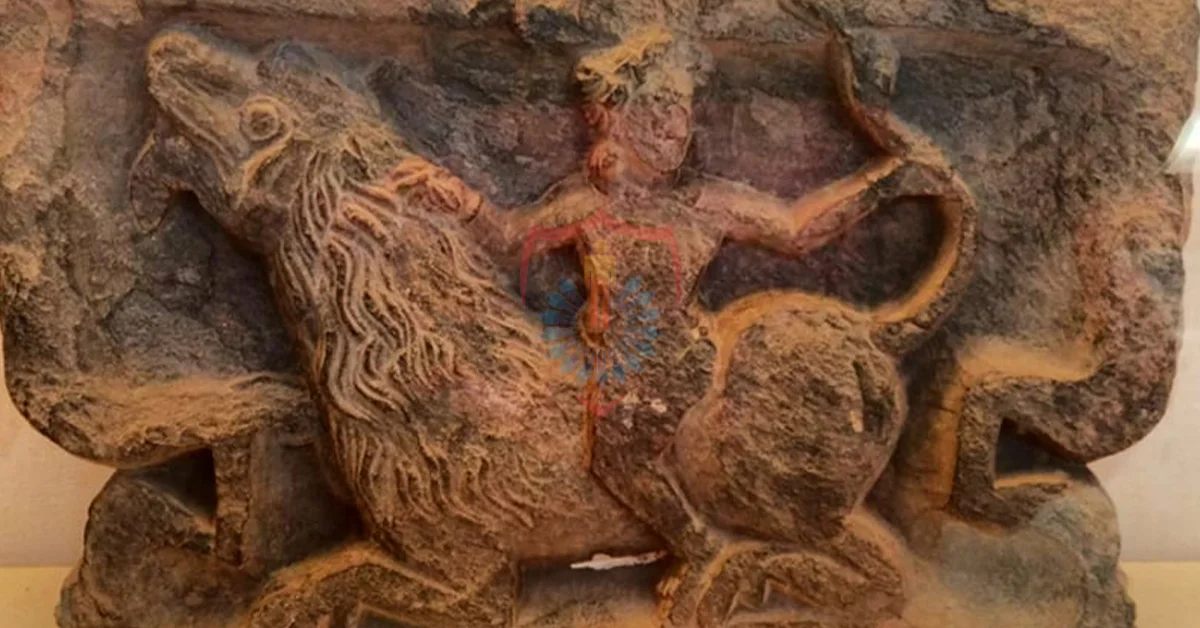

Modern scholars and art historians continue to study and research Gandhara art, unearthing new insights into its development and cultural context. The fascination with Gandhara’s artistic heritage has led to numerous academic publications and exhibitions, contributing to a deeper understanding of the region’s history and artistic achievements.
Beyond academia, Gandhara art has also influenced contemporary artists and designers. Elements of Gandhara’s artistic style can be seen in various forms of modern art, architecture, and fashion. The seamless blend of diverse cultural influences in Gandhara art continues to inspire creativity and innovation in the art world.
The preservation and promotion of Gandhara art have also been bolstered by cultural initiatives and international collaborations. Governments and cultural organizations are actively working to safeguard and showcase Gandhara’s artistic legacy, ensuring that future generations can appreciate and learn from this ancient artistic tradition.
Tourism and Education
Tourism can play a vital role in enhancing education and enriching the learning experiences of individuals. When travelers embark on journeys to explore new destinations, they are presented with unique opportunities to gain knowledge about diverse cultures, histories, and environments. Educational tourism goes beyond the traditional classroom setting, allowing students and enthusiasts to engage in immersive and experiential learning.
One of the primary ways tourism contributes to education is through cultural exchange. When travelers visit foreign countries, they have the chance to interact with local communities, partake in traditional customs, and experience authentic cultural practices. This firsthand experience fosters cultural awareness, empathy, and a broader global perspective, breaking down stereotypes and promoting mutual understanding.

Historical sites, like the ancient region of Gandhara in Pakistan, provide a living textbook for students and history enthusiasts. Walking amidst the ancient ruins and artifacts offers a tangible connection to the past, making history come alive. Such experiences inspire a deep interest in historical events and encourage individuals to delve deeper into the annals of time, cultivating a passion for learning.
Additionally, educational tourism opens the door to environmental awareness and sustainable practices. As travelers explore diverse ecosystems and natural wonders, they become more attuned to the need for conservation. Learning about the delicate balance of ecosystems and the threats they face fosters a sense of responsibility toward preserving our planet’s biodiversity.
Furthermore, educational institutions often incorporate educational trips and study tours as part of their curriculum. These experiential learning opportunities provide students with hands-on experiences related to their academic subjects, be it biology, geology, literature, or art history. Field trips to museums, historical sites, and ecological reserves reinforce classroom lessons and enable a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Gandhara Festival in Pakistan
The Gandhara Festival in Pakistan is a vibrant celebration of the rich cultural and historical heritage of the ancient Gandhara region. Held annually, this festival brings together locals, tourists, scholars, and artists to commemorate the legacy of Gandhara and showcase its profound contributions to art, history, and religion.
The festival serves as a platform for cultural exchange, as performers from different regions come together to showcase traditional music, dance, and art forms. Visitors have the opportunity to experience the colorful diversity of Pakistan’s cultural tapestry, from classical dance performances to folk music that echoes the traditions of the Gandhara era.
One of the highlights of the Gandhara Festival is the exhibition of Gandharan art and artifacts. Museums and archaeological sites open their doors to showcase some of the most exquisite sculptures and relics from the region’s illustrious past. Guided tours and lectures by experts offer insights into the historical significance of these artifacts and the artistic fusion that defined Gandharan art.
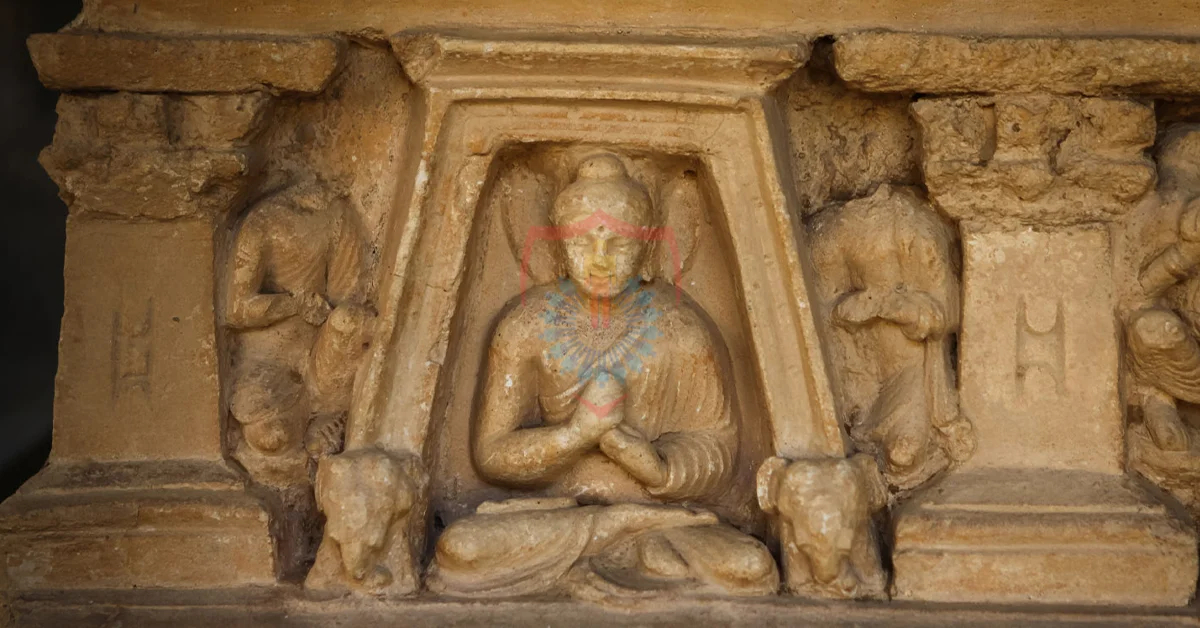

The festival also emphasizes the importance of preserving and conserving the cultural and archaeological treasures of Gandhara. Workshops and seminars are held to raise awareness about the need for responsible tourism and sustainable practices to safeguard these invaluable heritage sites for future generations.
Moreover, the Gandhara Festival acts as a bridge between the past and the present, fostering a renewed interest in the ancient region’s history. Through cultural performances, exhibitions, and interactive activities, the festival inspires a sense of pride and appreciation for Pakistan’s rich historical legacy.
In conclusion, the Gandhara Festival in Pakistan is a remarkable celebration of the ancient Gandhara civilization. It not only showcases the vibrant cultural heritage of the region but also encourages dialogue, understanding, and appreciation for the contributions of Gandhara to the world’s art and history. This annual event serves as a reminder of the enduring legacy of Gandhara and its importance in shaping Pakistan’s cultural identity.
Conclusion
As we venture into the realm of Gandhara, we unearth a treasure trove of art and history that has left an indelible mark on the world. The intricate sculptures, the grand stupas, and the Greco-Buddhist connections all serve as a testament to the brilliance of ancient Gandhara.
Today, as we rediscover Gandhara, we are reminded of the value of preserving our shared human heritage. The enduring legacy of this enigmatic land transcends time, encouraging us to appreciate the beauty of cultural diversity and the interplay of civilizations.
As we conclude this journey through the wonders of Gandhara, let us cherish the wisdom of the past and carry it forward into the future, preserving the essence of Gandhara for generations to come.
FAQs about Gandhara
Q1. What is Gandhara?
Gandhara was an ancient region located in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent, encompassing parts of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan. It was a prominent cultural and religious center known for its unique artistic style and historical significance.
Q2. What is Gandharan art?
Gandharan art is a distinctive artistic style that emerged in the region, blending Greek and Indian elements. It is renowned for its lifelike sculptures of Buddha and other Buddhist deities, reflecting the fusion of diverse cultural influences.
What is the significance of Gandhara in history?
Gandhara played a pivotal role in the spread of Buddhism to various parts of Asia and beyond. It was also an important crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, fostering a harmonious blend of civilizations.
Q3. How is Gandhara preserved today?
Efforts are underway to protect and restore Gandhara’s ancient sites and artifacts. Archaeological excavations continue to unearth new discoveries, while museums and educational institutions contribute to preserving and promoting its cultural heritage.
Q4. Why is Gandhara a popular destination for tourists?
Gandhara’s historical significance and its association with Buddhism attract travelers from around the world. Visitors can explore ancient Buddhist sites, marvel at the exquisite sculptures, and immerse themselves in the rich heritage of the region.
Q5. What is the Gandhara Festival in Pakistan?
The Gandhara Festival in Pakistan celebrates the region’s cultural heritage through various cultural events, art exhibitions, and performances. It serves as a platform to honor Gandhara’s artistic legacy and promote contemporary expressions of its beauty.
Our Featured Article:
Read More: Discover The Ancient Beauty of Gandhara: A Guide to Tourism in Pakistan
Read More: Pakistan Promotes Gandhara Art to Boost Tourism
Don’t miss the chance to invest with Lakeshore! Secure your investment today by investing your financial investment with Lakeshore in the following available options like Lakeshore City, Lakeshore Club, and Lakeshore Farms.
For More updates, please Contact +92 335 7775253 or visit our website https://lakeshorecity.com/
Lakeshore City is the upcoming elite lifestyle at Khanpur Dam. Offering no parallel amenities for the members and owners of distinguished farmhouses.
Become Part of Luxurious Lifestyle
Contact: 0335 7775253
