Introduction to Gandhara, Pakistan
Sections of Afghanistan and Pakistan still make up the historically significant region known as Gandhara. Due to its extensive religious and cultural past, particularly its connections to Buddhism and the historic trade routes that connected Central Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and the West, is of enormous historical significance.

Geographical Location
Gandhara is located northwest of the Indian subcontinent, mainly comprising portions of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of modern-day Pakistan and the northern parts of Afghanistan.
Historical Significance
The history of the Gandhara region is extensive and varied, dating back to antiquity. The Silk Road, a system of trade routes that promoted the movement of products, culture, and ideas between various civilizations, was famed for its strategic placement along it.
Gandhara Civilization
From roughly the sixth century BCE to the eleventh century CE, the ancient Gandhara civilization thrived there. Persian, Greek, Indian, and Central Asian influences were among the many cultures that came together to form this melting pot.

Buddhism in Gandhara
The relationship of Buddhism with Gandhara is particularly well-known. One of the first areas where Buddhism left the Indian subcontinent was there. The area became a significant hub for Buddhist art and culture, with several stupas, monasteries, and sculptures being constructed.
Gandharan Art
The distinctive art form known as Gandharan art is one of Gandhara’s greatest gifts to the world. These beautiful sculptures of Buddha and other Buddhist deities result from the fusion of Hellenistic and Indian artistic traditions.
Gandhara’s Decline
The area underwent several invasions and authority changes throughout the ages. The cultural environment of Gandhara was substantially altered by the waning of Buddhism and the ascent of Islam in the Indian subcontinent.
Archaeological Heritage
Today, visitors, historians, and archaeologists highly value Gandhara’s ancient ruins and archaeological sites. Excavations have uncovered priceless artifacts and buildings that provide insight into the area’s illustrious past.
Influence in the Present
Gandhara still influences the area’s culture. It still plays a crucial role in preserving Pakistan’s historical identity and fostering cultural tourism.
Historical Context: Tracing the Roots of Gandhara
The history of Gandhara may be traced back to when the area was a nexus for many different cultures and civilizations. The historical setting of Gandhara is complex, shaped by some occasions and contacts with other societies.
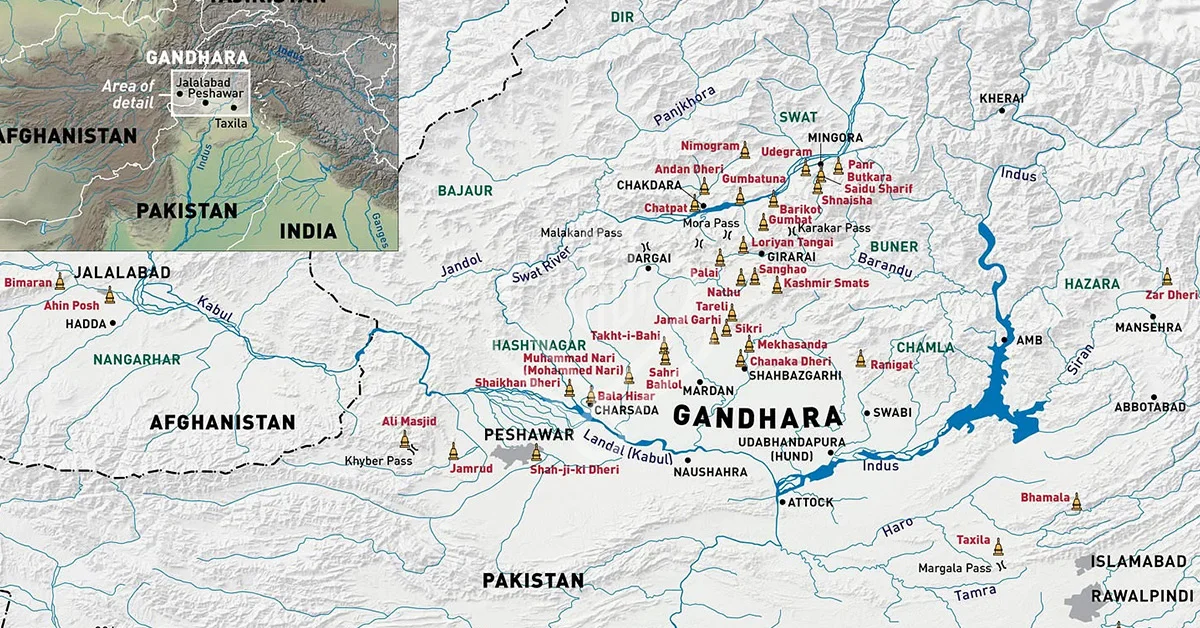
Indus Valley Civilization
Early inhabitants of the Gandhara region date back to the Indus Valley Civilization, which existed between 3300 and 1300 BCE. Indus Valley inhabitants developed complex urban communities and cultures in regions that include modern-day Pakistan and northwest India.
Aryan Migration
Around 1500 BCE, Indo-European tribes were carried to the Indian subcontinent by Aryan migrations from Central Asia. These migrations shaped the early Vedic traditions and the local society, impacting culture.
Persian Influence
Under the leadership of King Darius the Great, the Achaemenid Empire of Persia conquered the northwest areas of the Indian subcontinent, including Gandhara, in the sixth century BCE. This demonstrated the Persian impact on the society and government of the area.
Alexander the Great
Invading the Indian subcontinent in 327 BCE, Alexander the Great took control of the Gandhara region. His campaign significantly influenced the cultural contact between indigenous Indian cultures and the Greeks, developing Gandharan and Greco-Buddhist art.
Buddhism’s Expansion
The Indian subcontinent was not the only place where Gandhara’s influence could be felt. It developed into a Buddhist knowledge and culture hub, drawing researchers and travelers across Asia.
Kushan Empire
In the first century CE, the area was governed by the Kushan Empire, which had sway over northern India and Central Asia. The Kushans were outstanding patrons of the arts and contributed to the growth of Gandharan art.
White Huns and Decline
Buddhism in the area experienced a decrease due to the invasion of Gandhara by the White Huns, a nomadic Central Asian tribe, in the fifth century CE. Over the years, the area experienced numerous charges and changes of control.
Islamic Conquests
Gandhara’s cultural and religious landscape underwent a profound transformation in the seventh century CE with the introduction of Islam to the Indian subcontinent. As Buddhism declined, Islamic traditions grew more substantial in the area.
Influence of Gandhara on Art, Culture, and Civilization
Gandhara had a tremendous and broad impact on art, culture, and civilization. Due to the region’s unique location at the meeting point of numerous societies, including Greek, Persian, Indian, and Central Asian, a rich cultural exchange occurred that had a lasting effect on many facets of life.
Buddhist Art
Gandhara is well-known for its contributions to this field. As a result of the blending of Indian and Hellenistic creative traditions, the Gandharan art style developed. This merger produced beautiful statues of the Buddha and other Buddhist deities that harmoniously merged traditional Indian iconography with realistic elements inspired by Greece.
Stupa and Monastery Development
Gandhara became a key location for the development of stupas and monastic complexes. Buddhists used these buildings as sites of worship, meditation, and education. These buildings’ artistic and architectural breakthroughs impacted Buddhist architecture in other areas.
Trade and Economic Influence
Due to Gandhara’s advantageous location across the Silk Road, extensive trade between the East and the West was made possible. As traders, intellectuals, and travelers passed through Gandhara and exchanged commodities, concepts, and knowledge, thriving trade networks enhanced the area economically and culturally.
Buddhism’s Expansion
As a critical center for Buddhist knowledge and creativity, Gandhara was essential to the religion’s expansion outside the Indian subcontinent. The monasteries in the area drew intellectuals and travelers, assisting in spreading Buddhist teachings throughout Central Asia and into China.
Literature and Language
The cultural interactions in Gandhara impacted early Indian literature and language. Due to other cultures’ impact, the Sanskrit language developed and thrived in the area. Gandhara aided in the translation of Buddhist texts into many languages.
Coinage & Numismatics
The syncretic culture of Gandhara was reflected in the region’s production of distinctive and complex coins. Gandharan coins frequently portrayed kings, gods, and other figures from many cultural traditions.
Astronomy and Mathematics
Gandhara contributed to these two disciplines. Regional academics worked to improve mathematical theories and astronomy calculations.
Artistic Legacy and Global Impact
Later Buddhist art in Asia was greatly influenced by the Gandharan art style and its distinctive depictions of Buddha and bodhisattvas, as far away as Central Asia, China, and Southeast Asia, the art and culture of Gandhara have left their mark.

Economic Development Initiatives
With its extensive historical and cultural legacy, Gandhara provides various economic development initiatives focused on travel and tourism. The region is a tempting travel destination for visitors and history buffs alike due to its prominence as an early center of Buddhism and its distinctive fusion of Hellenistic and Indian influences in art and architecture.
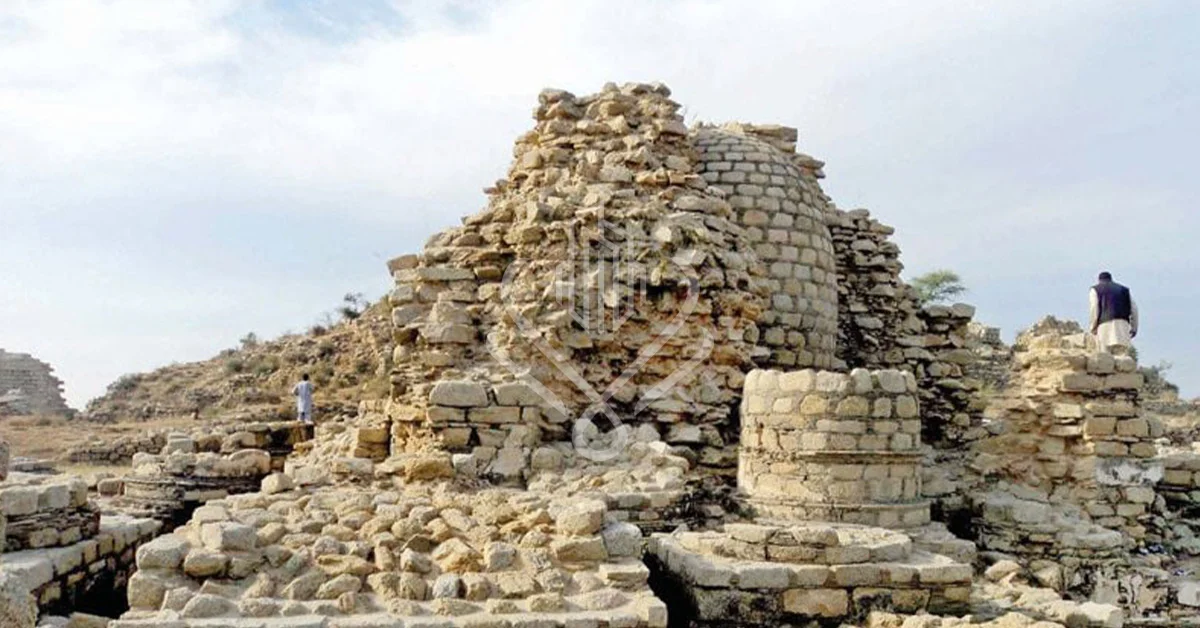

Initiatives related to “Gandhara Tourism and Travel” are intended to encourage the discovery of the region’s famous Buddhist sites, including the old stupas and monasteries, bringing both local and foreign tourists to experience the spiritual and cultural atmosphere of the past.
Gandhara Adventurous Cultural Heritages
Initiatives like “Gandhara Adventurous Cultural Heritages” cater to thrill-seekers by providing opportunities for exploration and trekking in Gandhara’s picturesque landscapes, letting visitors enjoy its mesmerising natural beauty. Additionally, “Ancient Mythology and Gems in Gandhara” initiatives can concentrate on promoting local crafts and jewellery industries, showcasing their intricate designs and the historical significance of gemstones in Gandhara’s trade history.

These initiatives recognize the region’s potential in ancient mythology and gemstones. In addition to providing income and job opportunities for the local populace, these coordinated initiatives to grow the economy also help protect and advance Gandhara’s priceless cultural legacy for future generations.
Infrastructure Development
For Gandhara’s economy to expand and its culture to be preserved, infrastructure development, particularly the enhancement of transport networks, the modernization of roads and highways, and the construction of airports and railway systems, offers enormous promise.

Improvement of Transportation Networks
Infrastructure development can be significant for encouraging tourism and aiding the exploration of Gandhara’s cultural treasures, an ancient territory of substantial historical value. The prominent Buddhist temples, stupas, and monasteries of Gandhara can be more easily accessed by travellers worldwide by strengthening transportation networks. By improving connectivity between different cities and archaeological sites in the area, modernising roads and highways can make it simpler for tourists to navigate and appreciate the region’s historical beauties.
Development of Airports and Railway Systems

Accessibility to Gandhara can be further improved by constructing airports and rail networks, making it a more alluring destination for domestic and international travellers. Effective transport connections can also attract investment to the area, fostering economic expansion and opening local job opportunities.
Additionally, with better transportation, the cultural history of Gandhara may be preserved and administered more effectively. The movement of specialists, archaeologists, and historians can be aided by adequate infrastructure, allowing them to collaborate to conserve and maintain the historical monuments and artefacts of the area.
Industrial Growth
Initiatives for industrial growth in Gandhara can be crucial for promoting economic progress and providing locals with employment possibilities. The government and appropriate authorities can support economic diversification and accelerate Gandhara’s overall economic growth by developing the region’s manufacturing and industrial sectors.

Promotion of Industries and Manufacturing Sectors
Creating industrial zones and business parks can act as specific locations for industrial activities, luring financiers and companies to set up shop. Placing these zones strategically close to transportation hubs will simplify carrying commodities into and out of the area. Furthermore, luring businesses to invest in Gandhara with alluring incentives and facilities within these zones can support the expansion of the local economy.
Attracting Foreign Investments
Foreign investments greatly aid industrial growth, and Gandhara may take advantage of this by fostering a supportive business climate and implementing investment-friendly regulations. Gandhara can draw foreign investors looking to take advantage of its distinctive qualities by highlighting the area’s rich historical and cultural history and its potential in several industries.
Technological Advancements
Technological development in Gandhara can promote innovation, preserve its historical and cultural heritage, and help the country advance economically and socially. The region must embrace digital transformation to enter the digital era and utilise technology’s capabilities in various sectors.

Gandhara can inspire young entrepreneurs and inventive minds to create new solutions, products, and services by encouraging startups and building innovation centres. These firms can concentrate on using technology to overcome regional problems, improve visitor experiences, and highlight the area’s rich cultural legacy on digital platforms.
Implementation of Innovative City Initiatives
Improvements in urban planning, effective public services, and increased connectivity can result from implementing innovative city initiatives in Gandhara. Smart city technologies can manage traffic congestion, optimise resource use, and encourage sustainable practices, ultimately improving the quality of life for locals and tourists.

Technology may also be instrumental in preserving and documenting Gandhara’s historical sites and artefacts. To make sure that the region’s cultural legacy is available to a worldwide audience, digital archiving, virtual reality tours, and interactive exhibitions can offer a singular and immersive experience for tourists and researchers.
Social Welfare and Human Development
Social welfare and human development initiatives are essential in Gandhara to improve community well-being, protect cultural assets, and foster inclusive progress. These programs should prioritise meeting the people’s social, economic, and educational needs while preserving and advancing Gandhara’s distinctive cultural character.

Education and Skill Development
Practical education and skill development programs must be funded to empower the local community. Access to education, career training, and digital literacy are three things that Gandhara can do to give its people the tools they need to engage in the modern economy and enhance their standard of living.

Healthcare and Public Services
It is essential for the community’s health that everyone has access to cost-effective, dependable healthcare. Gandhara can raise its citizens’ general health and living standards by enhancing its healthcare system and broadening access to care.

Preservation of Cultural Legacy
Activities aimed at preserving and promoting Gandhara’s cultural legacy should be a part of social welfare projects. Supporting efforts to preserve historical landmarks, museums, and cultural events can encourage a sense of local pride and identity and draw tourists interested in culture.
Poverty Alleviation
Implementing focused programs to combat poverty helps raise downtrodden groups in Gandhara. Marginalised people can escape poverty if social safety nets, microfinance possibilities, and income-generating ventures are available.
Women’s Empowerment
Women’s empowerment and promoting gender equality are crucial for developing an inclusive and forward-thinking society. Positive societal changes can result from initiatives that allow women to participate in the workforce, pursue education, and access healthcare.
Community Development
Community development can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for the advancement of the area by involving the local communities in decision-making processes and supporting community-driven development initiatives.
Healthcare and Public Services
In Gandhara, public services and healthcare are vital to maintaining the welfare of the populace and safeguarding the region’s cultural legacy. Gandhara can raise community living standards and advance social development by emphasising improving healthcare facilities and widening access to public services.
Accessible Healthcare Facilities
The inhabitants of Gandhara can have better access to high-quality healthcare services by investing in contemporary healthcare infrastructure, hospitals, and clinics. The region can guarantee that everyone receives prompt medical attention and treatment by offering medical facilities in urban centres and distant communities.
Preservation of Traditional Medicine
In addition to contemporary medical procedures, Gandhara may benefit by maintaining and advancing its traditional medical practices. A holistic approach to health and well-being that considers the area’s cultural history can be provided by fusing conventional therapeutic techniques with cutting-edge medical procedures.
Health Awareness and Education
Launching campaigns for health awareness and education can provide the local populace the power to decide what’s best for their health. Healthier lifestyles among the locals can be promoted by focusing on preventative healthcare, nutrition, and cleanliness practices.
Infrastructure for Public Services
Creating and enhancing infrastructure for public services, such as waste management, water supply, and sanitation systems, is essential for preserving a clean and sanitary environment in Gandhara. In addition to having a favourable effect on public health, this can help to protect the region’s cultural history.
Tourism and Heritage Preservation
Healthcare and public services programs should consider how tourism affects public health. It is possible to ensure that the flood of visitors does not jeopardise the health and well-being of the local populations by implementing sustainable tourism practices and measures to protect heritage assets.

Community Health Initiatives
Involving local groups in healthcare programs can encourage a sense of ownership and accountability for one’s health. Community health programs can address specific health issues, encouraging routine checkups and healthy habits.
Poverty Alleviation and Social Safety Nets
In line with the region’s cultural heritage and values, poverty reduction and social safety nets in Gandhara are crucial in uplifting underprivileged communities and safeguarding their well-being.

Empowering Local Communities
Initiatives to reduce poverty in Gandhara should empower local communities by giving them opportunities for skill improvement, vocational training, and income-generating ventures. These initiatives can help marginalised people escape poverty by encouraging self-reliance and entrepreneurship.
Inclusive Growth
To safeguard aged, disabled, and marginalised people in Gandhara from economic shocks and to ensure that they have access to essential services, social safety nets are required. Inclusive and social fairness growth can be achieved by improving healthcare, education, and social services.
Preservation of Traditional Livelihoods
To reduce poverty, it is essential to maintain the customs that have supported the communities in Gandhara for many years. Supporting traditional artists and crafters can contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage and help these people live more sustainably.
Community Support and Solidarity
Gandhara’s cultural ideals highly value community support and solidarity. Social safety nets can be strengthened, ensuring that society’s most vulnerable people are cared for and safeguarded through encouraging cooperative ventures and community-based projects.
Responsible Tourism
When appropriately managed, tourism in Gandhara can also help reduce poverty. The economic status of the locals can be improved by programs that support community-based tourism, where the local populace profits from tourism-related activities.
Environmental Conservation and Sustainability
The preservation of Gandhara’s natural beauty and unique biodiversity, in keeping with the area’s cultural history and ecological values, depends on environmental sustainability and conservation.

Conservation of Natural Resources
Protecting Gandhara’s natural resources, such as its forests, waterways, and minerals, should be the primary goal of the country’s environmental activities. Future generations can be guaranteed that these resources will be available for the foreseeable future through sustainable practices, including reforestation, afforestation, and ethical mining.

Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystems
The flora and fauna of Gandhara are diverse, with certain species being endangered or fragile. The region’s biodiversity and vulnerable ecosystems can be conserved by implementing wildlife conservation programs, creating protected areas, and encouraging responsible tourism.
Sustainable Land Use and Forest Management
Responsible land use planning is essential to stop Gandhara deforestation, habitat loss, and soil degradation. Sustainable forest management techniques can sustain regional communities that rely on the forests’ resources while helping preserve the natural balance.

Water Resource Management
Effective water resource management is crucial in a place like Gandhara, where water shortage can be problematic. Water-related problems can be reduced by implementing conservation measures, encouraging water collection, and ensuring that water is distributed fairly.
Promoting Renewable Energy
To lessen its carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels, Gandhara can switch to renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydropower. Promoting clean energy usage can aid in sustainable development and environmental preservation.
Renewable Energy and Climate Action
Promoting renewable energy and climate action is essential in the context of Gandhara to ensure sustainable development while protecting its distinctive cultural and environmental heritage. Due to its historical importance and abundant natural beauty, Gandhara is responsible for embracing ecologically friendly behaviours and supporting regional and international efforts to mitigate climate change.
Gandhara’s dependence on fossil fuels can be considerably reduced, and greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by embracing renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydropower. Gandhara can help mitigate the effects of climate change, save its ecosystems, and promote a cleaner and greener environment for its residents and visitors by investing in infrastructure for renewable energy sources.

In addition, options for adopting climate action in Gandhara include planning for sustainable land use, reforestation, and wildlife preservation. The ecological balance of the area and the health of its distinctive flora and animals depend heavily on preserving biodiversity and natural habitats.
The local communities can also be empowered to take an active role in conserving their environment through increasing awareness of climate change and environmental protection. Supporting environmentally friendly trash disposal methods, water resource management, and agriculture can significantly lessen Gandhara’s Ecological Impact.
Collaboration and International Relations
To achieve a sustainable and eco-friendly future in Gandhara that is consistent with the cultural and environmental values of the area, it is crucial to promote renewable energy sources and implement climate action programs.
With its historical significance and stunning natural surroundings, Gandhara is well-positioned as a model for embracing renewable energy sources. Gandhara may lessen its reliance on fossil fuels, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and lessen the effects of climate change by utilising solar, wind, and hydropower. It is consistent with Gandhara’s historical appreciation for nature and its peaceful coexistence with the environment to emphasise using clean and renewable energy.

Implementing numerous steps to safeguard Gandhara’s distinctive ecosystems and biodiversity is necessary to mitigate the effects of climate change there. Planning for sustainable land use and planting trees can help protect open areas and natural ecosystems, ensuring a healthy and prosperous environment. By preserving its ecological resources, Gandhara can support national and international efforts to conserve the climate.
Another crucial component of Gandhara’s climate action plan is lowering carbon emissions. Promoting waste management, eco-friendly transportation methods, and energy-efficient practices can be essential to reduce carbon emissions. Gandhara can serve as a model for sustainable living and conscientious consumption by encouraging ecologically responsible behaviour.
Conclusion
Finally, Gandhara Development 2023 represents a critical turning point in Pakistan’s progress and innovation. Gandhara is positioned to emerge as a symbol of prosperity and harmony, emphasising sustainable growth, cultural preservation, and technical breakthroughs. Gandhara is adopting a balanced strategy that respects its ancient traditions while embracing the future through projects encouraging renewable energy, climate action, social welfare, and economic progress.
The region is dedicated to maintaining its stunning natural surroundings and rich cultural legacy, as evidenced by its work to safeguard biodiversity, promote responsible travel, and involve residents in development initiatives. The development in Gandhara is an example for other areas to follow since it is firmly based on living in harmony with nature and respecting its historical significance.
FAQs
Q1. What are the key sectors driving Gandhara’s development?
Ans. Key sectors driving Gandhara’s development include tourism, infrastructure, and renewable energy, focusing on leveraging its cultural heritage and natural beauty for economic growth.
Q2. How is the government promoting sustainable practices?
Ans. The government is promoting sustainable practices in Gandhara through initiatives like renewable energy adoption, eco-friendly tourism, and conservation efforts to protect its unique ecosystems.
Q3. What steps are being taken to preserve cultural heritage?
Ans. Steps taken to preserve cultural heritage in Gandhara include the restoration of historical sites, the establishment of museums, and educational programs to raise awareness about the region’s rich history.
Q4. What are the plans for Gandhara’s development?
Ans. Plans for Gandhara’s development involve further investment in infrastructure, sustainable tourism, and technology-driven initiatives to create a prosperous and environmentally conscious region.
Our Featured Article:
Read More: Discover The Ancient Beauty of Gandhara: A Guide to Tourism in Pakistan
Read More: Pakistan Offers ‘Huge Potential’ for Gandhara Tourism
Don’t miss the chance to invest with Lakeshore! Secure your investment today by investing your financial investment with Lakeshore in the following available options like Lakeshore City, Lakeshore Club, and Lakeshore Farms.
For More updates, please Contact +92 335 7775253 or visit our website https://lakeshorecity.com/
Lakeshore City is the upcoming elite lifestyle at Khanpur Dam. Offering no parallel amenities for the members and owners of distinguished farmhouses.
Become Part of Luxurious Lifestyle
Contact: 0335 7775253
